Cambria FTC Color Space Conversion
Table of Contents
- Preface
- HDR Standards
- Handling Wide Color Gamut
- FTC Handling of Color Related Metadata
- Case Study 1: SD/HD conversions (BT.601/BT.709)
- Case Study 2: HDR conversions (HLG/PQ)
- Case Study 3: SDR to HDR conversions (BT.709 to HLG/PQ)
- Case Study 4: HDR to SDR conversions (PQ/HLG to BT.709)
- Special Handling of MP4 Muxer
- Special Handling of X265 Encoder
Preface
Color Space conversion is always an important part of any transcoding process. Legacy workflows of SD/HD conversions, include BT.601 and BT.709, which are often converted back and forth. In modern SDR/HDR workflows, we often need to convert between BT.709 and various HDR color spaces, namely PQ, HLG, etc.
Cambria File Convert supports these conversions during the transcoding process, using various available source/target filters.
HDR Standards
Before converting color spaces between HDR formats, it is important to understand the different HDR standards. HDR implies a larger range of minimum and maximum luminance (brightness) and wide color gamut. Cambria FTC supports conversion between the following HDR standards:
- PQ: SMPTE BT.2084/BT.2100, also known as HDR10/HDR10+
- HLG: ARIB STD-B67, or SMPTE BT.2100
- Dolby Vision (via Dolby Vision license, see separate document)
Handling Wide Color Gamut
There is no special conversion needed. If your target is HLG/PQ via the Color Space Conversion filter, BT.2020 color space will be used implicitly.
You may want to use a format that retains color precision:
- 10/12-bit bit depth
- 4:2:2 / 4:4:4 Color Format (4:4:4 can be via MOV ProRes)
If you are just interested in converting from SD/HD in BT.709 to UHD/4K in BT.2020 color space, you can use “Case Study 2” below, and select BT.709 to BT.2020. This is a rare workflow though.
Handling Color Related Metadata
Converting between SDR and HDR involves multiple steps:
- Apply Color Space Conversion Filter (or related filter).
- Set proper Color Primaries, Transfer Characteristics, and Matrix Coefficients in Video Settings (except for X265, which requires command-line options).
- Enable "Write Color Info" in Container Format Settings (MP4 only).
During SDR/HDR conversions, only colors, luminance, and mappings are performed as necessary. There is no detection nor injection of additional static/dynamic metadata, such as HDR10/HDR10+. If you are converting to X265, you can add static metadata via Extra Options as command lines.
**Actual workflow examples are described in below sections
Case Study 1: SD/HD Conversions (BT.601/BT.709)
-
In Preset Editor, add the 601/709 Correction video filter.
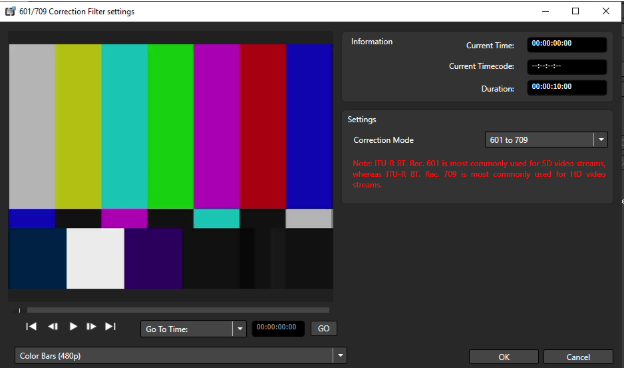
-
The filter can be applied as a source or target filter, but applying it as a source filter is more efficient.
-
In Video Settings (Encoding Tab), select Color Primaries, Transfer Coefficients, and Matrix Coefficients in Video Settings in the Encoding Tab of the Preset Editor Window:
Note: This conversion has loss and is not perfectly reversible.
Case Study 2: HDR Conversions (HLG/PQ)
This case is about converting between HLG and PQ. This conversion is reversible. Unlike Case Study 1, we select Color Space Conversion Filter:
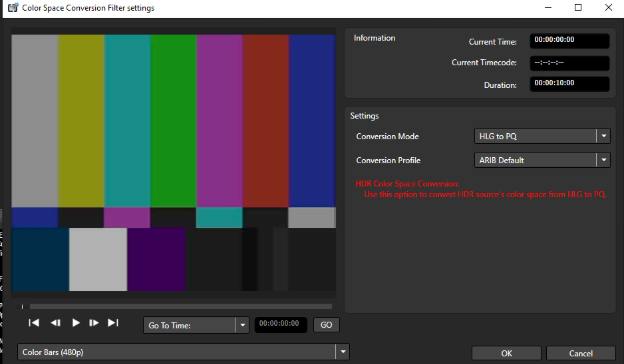
The filter can be added as a source or target filter. However, this is more efficient and accurate as a source filter..
Then, select proper Color Primaries, Transfer Coefficients and Matrix Coefficients in Video Settings in the Encoding Tab of the Preset Editor Window:
Case Study 3: SDR to HDR Conversions (BT.709 to HLG/PQ)
This is similar to Case Study 2 in setup, just choose “BT.709 to HLG” in “Conversion Mode”. If you want to convert BT.709 to PQ, you can add an additional Color Space Conversion filter, and convert HLG to PQ.
Similarly, you also need to select proper Color Primaries, Transfer Coefficients and Matrix Coefficients in Video Settings in the Encoding Tab of the Preset Editor Window:
Case Study 4: HDR to SDR Conversions (PQ/HLG to BT.709)
While this is also similar to Case Study 2 and 3 in setup, as well as selecting proper Color Primaries, Transfer Coefficients and Matrix Coefficients in Video Settings, this is a highly controversial case.
First of all, as you can foresee, there are lots of data loss in such conversion, because, PQ/HLG (BT.2020 color space) is much larger than BT.709, and to achieve satisfactory conversion results, tone mapping algorithm is also used.
Currently, FTC is using a modified version of the Hable algorithm and is very conservative in nature. We are investigating to expose more options for users to fine tune the parameters, as well as using other well known algorithms, such as Reinhard.
Note: Future versions may allow users to fine-tune Reinhard or other tone mapping algorithms.
Special Handling of MP4 Muxer
BBy default, the color information that was set in Video Settings will be applied to the container as well, and there is no separate color information setting in Container Format Settings section.
The only exception is MP4 Muxer. To retain maximum compatibility with hardware players with our MP4 outputs, FTC does not write color information metadata by default (as well as not writing other metadata, but not described in this document). Hence, if your output is MP4 and when your players have no such issue, you should also write color information to the container as well (the example is PQ):
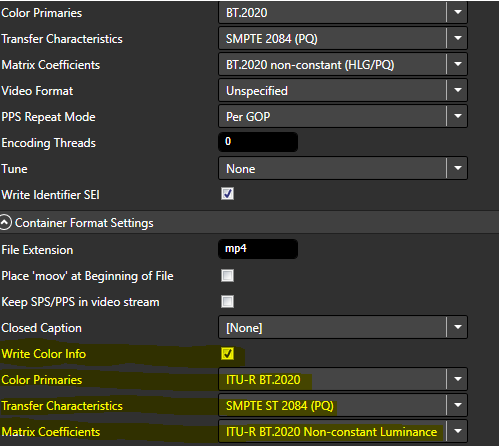
Special Handling of X265 Encoder
The X265 encoder has numerous settings configured via Extra Options, including color information.
Example settings for PQ encoding:
For HDR10 encoding, configure MaxCLL and MaxFALL via:
--max-cll <value>
Note: FTC does not measure or relay these values from the source. Users must manually input them.